Instrument – Chapter 3 – Navigation Systems
Quiz Summary
0 of 79 questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 79 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 79
1. Question
Which distance is displayed by the DME indicator?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 79
2. Question
Which DME indication should you receive when you are directly over a VORTAC site at approximately 6,000 feet AGL?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 79
3. Question
The greatest DME indication error between actual ground distance and displayed ground distance occurs at
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 79
4. Question
As a rule of thumb, to minimize DME select range error, how far from the facility should you be to consider the reading as accurate?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 79
5. Question
To find the VOR receiver ground checkpoint(s) for an accuracy check, which publication should you consult?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 79
6. Question
When flying directly over a published airborne VOR checkpoint, what is the maximum error allowed for IFR flight?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 79
7. Question
When using VOT to make a VOR receiver check, the CDI should be centered and the OBS should indicate that the aircraft is on the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 79
8. Question
When making an airborne VOR check, what is the maximum allowable tolerance between the two indicators of a dual VOR system (units independent of each other except the antenna)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 79
9. Question
When the CDI needle is centered during an airborne VOR check, the omni-bearing selector and the TO/FROM indicator should read
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 79
10. Question
Refer to figure 81 below. When checking a dual VOR system by use of a VOT, which illustration indicates the VOR’s are satisfactory?
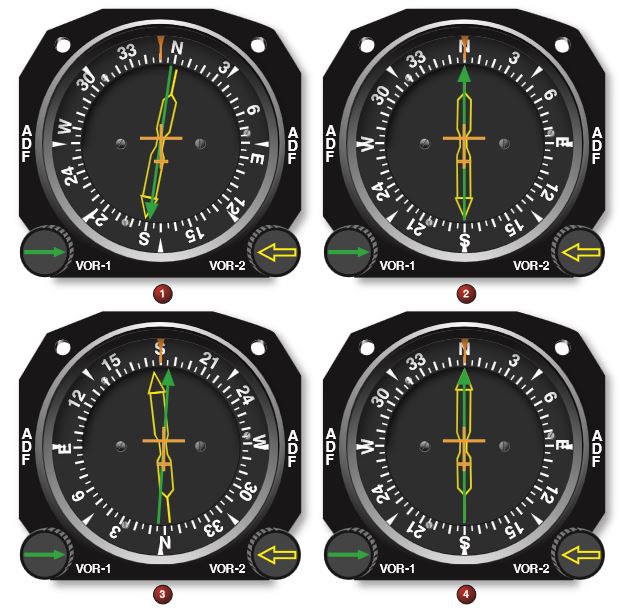 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 79
11. Question
While airborne, what is the maximum permissible variation between the two indicated bearings when checking one VOR system against the other?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 79
12. Question
Refer to figure 82 below. Which is an acceptable range of accuracy when performing an operational check of dual VORs using one system against the other.
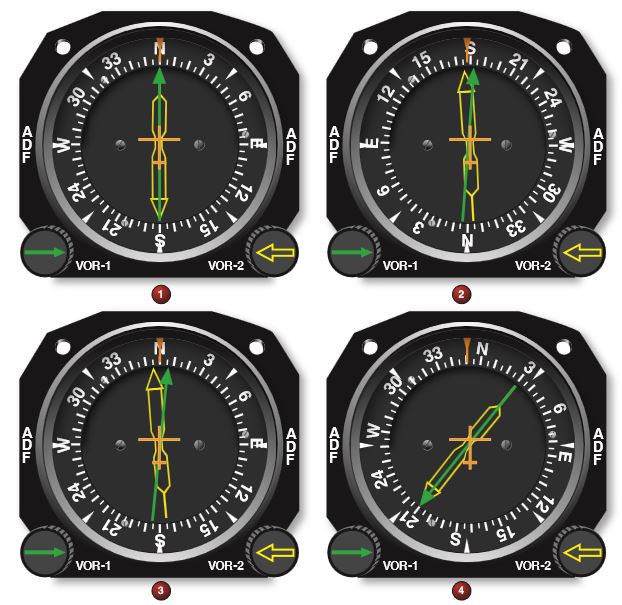 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 79
13. Question
How should the pilot make a VOR receiver check when the aircraft is located on the designated checkpoint on the airport surface?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 79
14. Question
Where can the VOT frequency for a particular airport be found?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 79
15. Question
Which indications are acceptable tolerances when checking both VOR receivers by use of the VOT?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 79
16. Question
What indication should a pilot receive when a VOR station is undergoing maintenance and may be considered unreliable?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 79
17. Question
A particular VOR station is undergoing routine maintenance. This is evidenced by
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 79
18. Question
When a VOR/DME is collocated under frequency pairings and the VOR portion is inoperative, the DME identifier will repeat at an interval of
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 79
19. Question
What is the meaning of a single coded identification received only once approximately every 30 seconds from a VORTAC?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 79
20. Question
For operations off established airways at 17,000 feet MSL in the contiguous U.S., (H) Class VORTAC facilities used to define a direct route of flight should be no farther apart than
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 79
21. Question
You are planning an IFR flight off established airways below 18,000 feet MSL. If you use VOR navigation to define the route, the maximum distance between NAVAIDs should be
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 79
22. Question
What angular deviation from a VOR course centerline is represented by a full-scale deflection of the CDI?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 79
23. Question
Full scale deflection of a COi occurs when the course deviation bar or needle
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 79
24. Question
When using VOR for navigation, which of the following should be considered as station passage?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 79
25. Question
Which of the following should be considered as station passage when using VOR?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 79
26. Question
When checking the sensitivity of a VOR receiver, the number of degrees in course change as the OBS is rotated to move the COi from center to the last dot on either side should be between
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 79
27. Question
A VOR receiver with normal five-dot course sensitivity shows a three-dot deflection at 30 NM from the station. The aircraft would be displaced approximately how far from the course centerline?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 79
28. Question
An aircraft which is located 30 miles from a VOR station and shows a 1/2 scale deflection on the COi would be how far from the selected course centerline?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 79
29. Question
Refer to figure 106 below. The course selector of each aircraft is set on 360 degrees. Which aircraft would have a FROM indication on the TO/FROM indicator and the CDI pointing left of center?
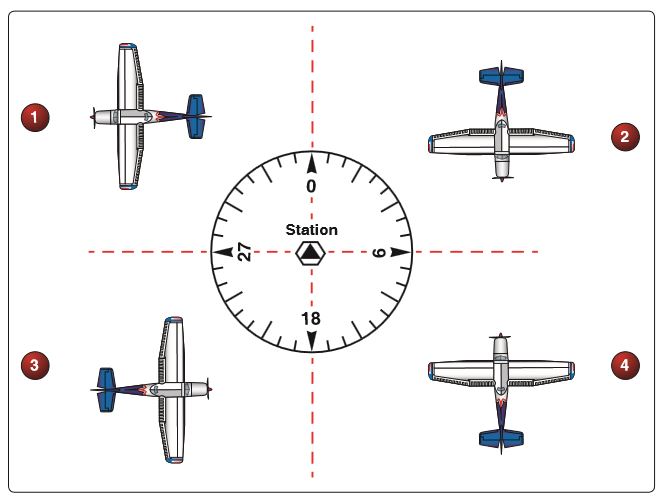 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 79
30. Question
Refer to figure 106 below. The course selector of each aircraft is set on 360 degrees. Which aircraft would have a FROM indication on the TO/FROM indicator and the CDI pointing right of center?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 79
31. Question
After passing a VORTAC, the CDI shows 1/2 scale deflection to the right. What is indicated if the deflection remains constant for a period of time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 79
32. Question
What angular deviation from a VOR course centerline is represented by a 1/2 scale deflection of the CDI?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 79
33. Question
Determine the approximate time and distance to a station if a 5 degree wingtip bearing change occurs in 1.5 minutes with a true airspeed of 95 knots.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 79
34. Question
Refer to figure 109 below. In which general direction from the VORTAC is the aircraft located?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 79
35. Question
Refer to figure 110 below. In which general direction from the VORTAC is the aircraft located?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 79
36. Question
Refer to figure 111 below. In which general direction from the VORTAC is the aircraft located?
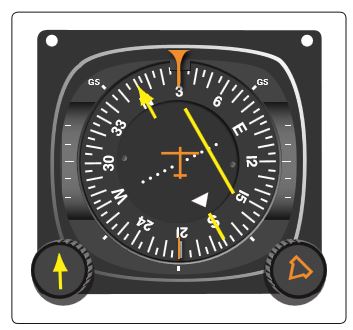 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 79
37. Question
Refer to figure 95 below. What is the lateral displacement of the aircraft in NM from the radial selected on the No. 1 NAV?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 79
38. Question
Refer to figure 95 below. On which radial is the aircraft as indicated by the No. 1 NAV?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 79
39. Question
Refer to figure 95 below. Which OBS selection on the No. 1 NAV would center the CDI and change the ambiguity indication to a TO?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 79
40. Question
Refer to figure 95 below. What is the lateral displacement in degrees from the desired radial on the No. 2 NAV?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 79
41. Question
Refer to figure 95 below. Which OBS selection on the No. 2 NAV would center the CDI?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 79
42. Question
Refer to figure 95 below. Which OBS selection on the No. 2 NAV would center the CDI and change the ambiguity indication to a TO?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 79
43. Question
Refer to figure 98 and figure 99 below. To which aircraft position does HSI presentation “A” correspond?
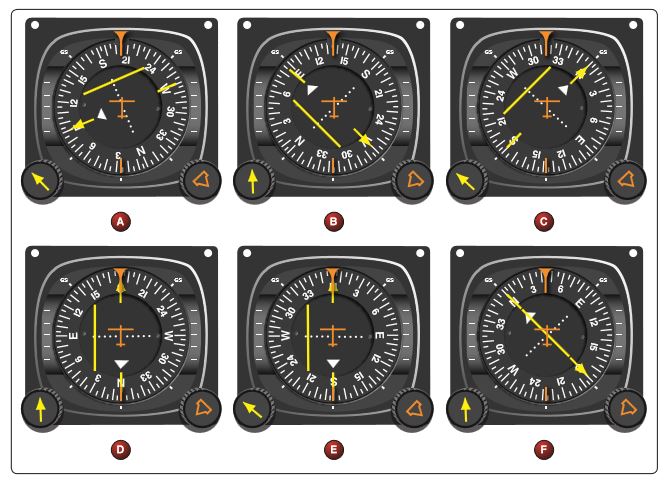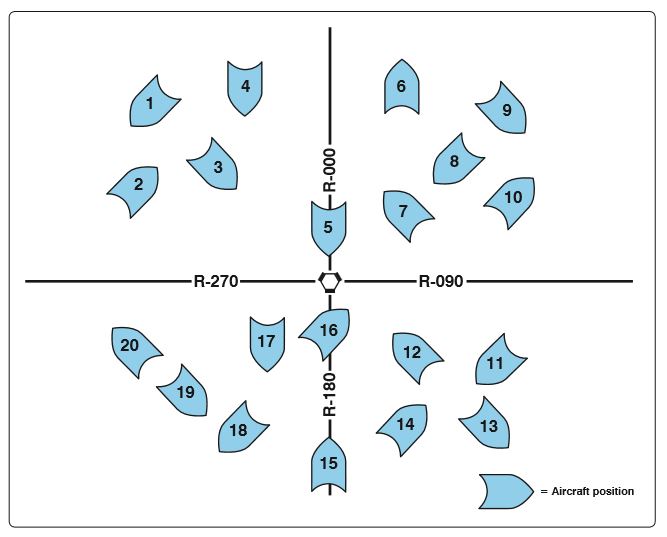
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 79
44. Question
Refer to figure 98 and figure 99 below. To which aircraft position does HSI presentation “B” correspond?

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 79
45. Question
Refer to figure 98 and figure 99 below. To which aircraft position does HSI presentation “C” correspond?

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 79
46. Question
Refer to figure 98 and figure 99 below. To which aircraft position does HSI presentation “D” correspond?

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 79
47. Question
Refer to figure 98 and figure 99 below. To which aircraft position does HSI presentation “E” correspond?

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 79
48. Question
Refer to figure 98 and figure 99 below. To which aircraft position does HSI presentation “F” correspond?

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 79
49. Question
Refer to figure 96 and figure 97 below. To which aircraft position(s) does HSI presentation “A” correspond? NOTE: HSI presentations B, C, D, E and I have backcourse settings of 090 degrees, which means there is reverse sensing irrespective of the airplane’s heading
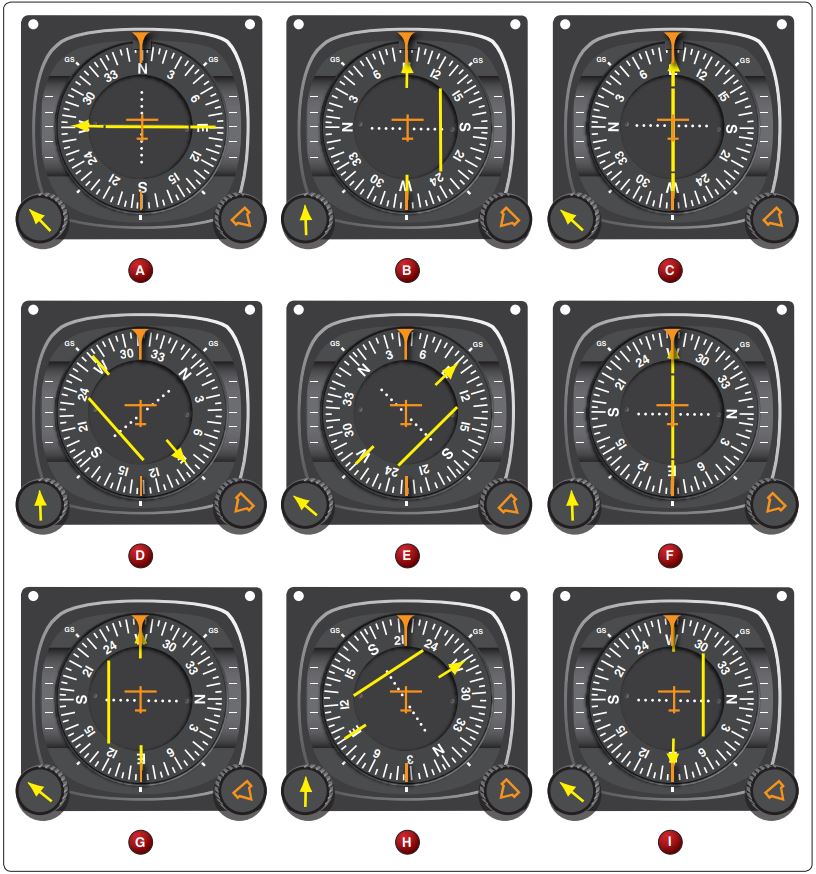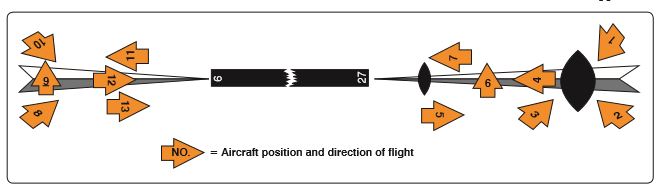
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 79
50. Question
Refer to figure 96 and figure 97 below. To which aircraft position(s) does HSI presentation “B” correspond? NOTE: HSI presentations B, C, D, E and I have backcourse settings of 090 degrees, which means there is reverse sensing irrespective of the airplane’s heading

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 51 of 79
51. Question
Refer to figure 96 and figure 97 below. To which aircraft position(s) does HSI presentation “C” correspond? NOTE: HSI presentations B, C, D, E and I have backcourse settings of 090 degrees, which means there is reverse sensing irrespective of the airplane’s heading

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 79
52. Question
Refer to figure 96 and figure 97 below. To which aircraft position(s) does HSI presentation “D” correspond? NOTE: HSI presentations B, C, D, E and I have backcourse settings of 090 degrees, which means there is reverse sensing irrespective of the airplane’s heading

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 53 of 79
53. Question
Refer to figure 96 and figure 97 below. To which aircraft position(s) does HSI presentation “G” correspond? NOTE: HSI presentations B, C, D, E and I have backcourse settings of 090 degrees, which means there is reverse sensing irrespective of the airplane’s heading.



 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 79
54. Question
Refer to figure 96 and figure 97 below. To which aircraft position(s) does HSI presentation “F” correspond? NOTE: HSI presentations B, C, D, E and I have backcourse settings of 090 degrees, which means there is reverse sensing irrespective of the airplane’s heading.

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 55 of 79
55. Question
Refer to figure 96 and figure 97 below. To which aircraft position(s) does HSI presentation “E” correspond? NOTE: HSI presentations B, C, D, E and I have backcourse settings of 090 degrees, which means there is reverse sensing irrespective of the airplane’s heading.

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 56 of 79
56. Question
Refer to figure 96 and figure 97 below. To which aircraft position(s) does HSI presentation “H” correspond? NOTE: HSI presentations B, C, D, E and I have backcourse settings of 090 degrees, which means there is reverse sensing irrespective of the airplane’s heading

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 57 of 79
57. Question
Refer to figure 96 and figure 97 below. To which aircraft position(s) does HSI presentation “I” correspond? NOTE: HSI presentations B, C, D, E and I have backcourse settings of 090 degrees, which means there is reverse sensing irrespective of the airplane’s heading

 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 58 of 79
58. Question
How can a pilot determine if a Global Positioning System (GPS) installed in an aircraft is approved for IFR en route and IFR approaches?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 59 of 79
59. Question
Hand-held GPS systems, and GPS systems certified for VFR operation, may be used during IFR operations as
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 60 of 79
60. Question
When may VFR waypoints be used in IFR flight plans?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 61 of 79
61. Question
During IFR en route and terminal operations using an approved TS0-C129 or TS0-C196 GPS system for navigation, ground based navigational facilities
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 62 of 79
62. Question
During IFR en route operations using an approved TSO-C129 or TSO-C196 GPS system for navigation,
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 63 of 79
63. Question
What are the primary benefits of satellite-based area navigation (RNAV)?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 64 of 79
64. Question
A handbook GPS is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 65 of 79
65. Question
Effective navigation by means of GPS includes
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 66 of 79
66. Question
Why should pilots understand how to cancel entries made on a GPS?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 67 of 79
67. Question
Reliance on GPS units
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 68 of 79
68. Question
Before a pilot utilizes a GPS route or procedure, what would be an acceptable method of verifying the GPS database is current?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 69 of 79
69. Question
When your aircraft is equipped with a TS0-C129 or TS0-C196 GPS, an airport may not be qualified for alternate use if
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 70 of 79
70. Question
When planning an IFR flight using GPS, the pilot should know that VFR waypoints
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 71 of 79
71. Question
Prior to using GPS waypoints for RNAV, what can you do to check the current status of the GPS database?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 72 of 79
72. Question
While conducting a GPS approach, if you disengage the auto sensitivity, what will occur?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 73 of 79
73. Question
GPS systems certified for IFR operations cannot be used as a substitute for DME receivers
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 74 of 79
74. Question
When using a TSO-C129 or TSO-C196 GPS for navigation and instrument approaches, any required alternate airport must have
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 75 of 79
75. Question
Your aircraft is equipped with a WMS enabled GPS unit. While performing a GPS approach, you note an “LNAVN NAV available” indication on the moving map display and horizontal situation indicator. You know that
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 76 of 79
76. Question
Aircraft operating under IFR with TSO-C129 or TS0-C196 GPS for en route navigation must also have installed
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 77 of 79
77. Question
Which of the following is a benefit of flying with an autopilot?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 78 of 79
78. Question
In an autopilot-controlled system, what device actually moves the control surfaces?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 79 of 79
79. Question
To ensure situational awareness while using an autopilot system
CorrectIncorrect