cfi Airplanes and Aerodynamics
Quiz Summary
0 of 110 questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 110 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 110
1. Question
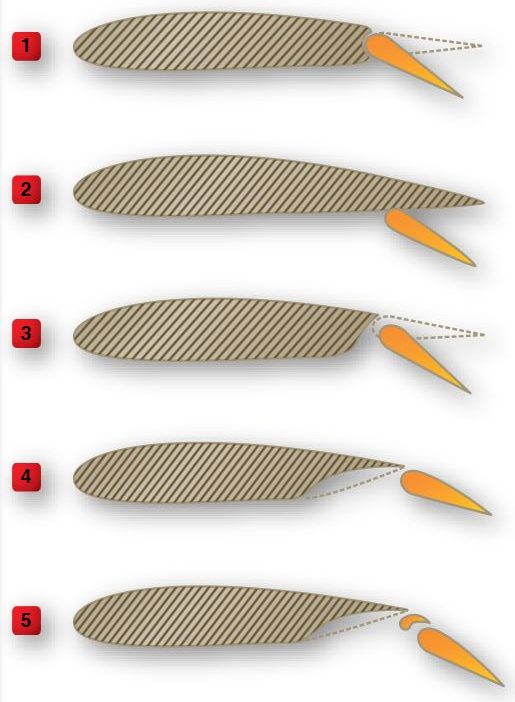
Refer to the diagram below. Which is a fowler flap?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 110
2. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which is a slotted flap?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 110
3. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which is a split flap?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 110
4. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which type of flap creates the greatest change in pitching moment?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 110
5. Question
Which type of flap creates the least change in pitching moment?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 110
6. Question
Which type of flap is characterized by large increases in lift coefficient with minimum changes in drag?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 110
7. Question
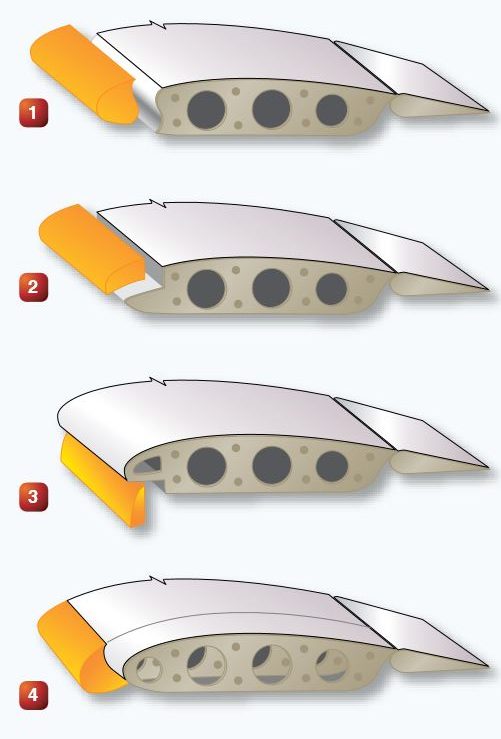
Refer to the diagram below. Which of the following illustrations is a fixed slot?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 110
8. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which of the following illustrations is a movable slot?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 110
9. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which of the following illustrations is a leading edge cuff?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 110
10. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which of the following illustrations is a leading edge flap?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 110
11. Question
Which statement relates to Bernoulli’s principle?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 110
12. Question
An aircraft wing is designed to produce lift resulting from
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 110
13. Question
During flight with zero angle of attack, the pressure along the upper surface of a wing would be
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 110
14. Question
Why does increasing speed also increase
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 110
15. Question
Lift produced by an airfoil is the net force developed perpendicular to the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 110
16. Question
The point on an airfoil through which lift acts is the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 110
17. Question
Changes in the center of pressure of a wing affect the aircraft’s
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 110
18. Question
When the angle of attack of a symmetrical airfoil is increased, the center of pressure will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 110
19. Question
An airplane would have a tendency to nose up and have an inherent tendency to enter a stalled condition when the center of pressure is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 110
20. Question
The force which imparts a change in the velocity of a mass is called
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 110
21. Question
That portion of the aircraft’s total drag created by the production of lift is called
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 110
22. Question
Airflow from two adjacent surfaces that merge and create eddy currents, turbulence, or restrict airflow is called
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 110
23. Question
As airspeed increases in level flight, total drag of an aircraft becomes greater than the total drag produced at the maximum lift/drag speed because of the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 110
24. Question
As airspeed decreases in level flight, total drag of an aircraft becomes greater than the total drag produced at the maximum lift/drag speed because of
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 110
25. Question
Which relationship is correct when comparing drag and airspeed?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 110
26. Question
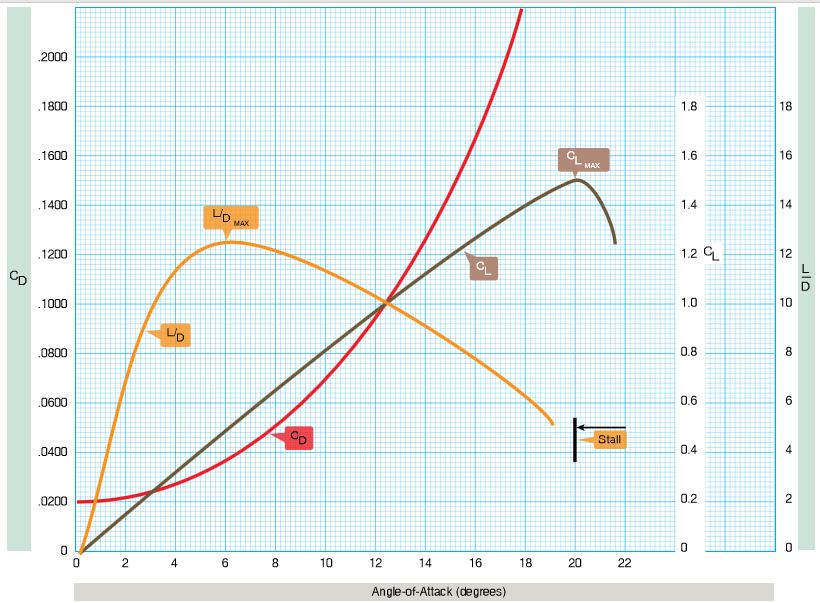
Refer to the diagram below. Which statement is true regarding airspace flight at L/Dmax?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 110
27. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The lift/drag at 2 degree angle of attack is approximately the same as the lift/drag for
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 110
28. Question
Refer to the diagram below. At which angle of attack does the airplane travel the maximum horizontal distance per foot of altitude lost?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 110
29. Question
Maximum gliding distance of an aircraft is obtained when
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 110
30. Question
If an increase in power tends to make the nose of an airplane rise, this is the result of the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 110
31. Question
When considering the forces acting upon an airplane in straight-and-level flight at constant airspeed, which statement is correct?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 110
32. Question
Which statement is true regarding the forces acting on an airplane in a steady-state climb?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 110
33. Question
During a steady climb, the rate of climb depends on
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 110
34. Question
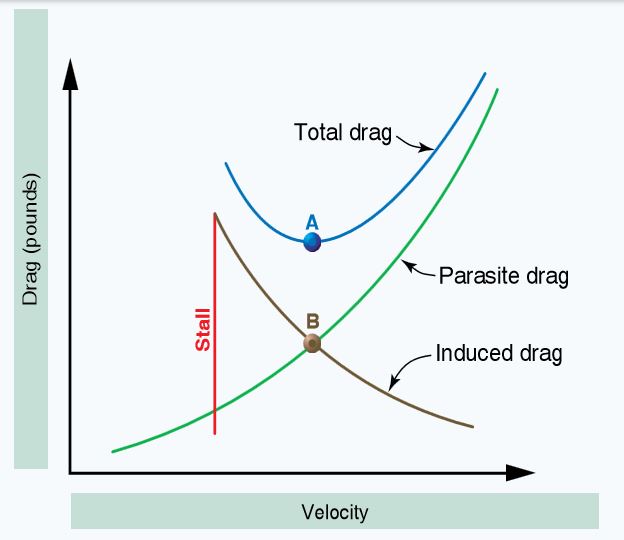
Refer to the diagram below. At the airspeed represented by point A, in steady flight, the aircraft will
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 110
35. Question
Refer to the diagram below. At an airspeed represented by point B, in steady flight, the pilot can expect to obtain the aircraft’s
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 110
36. Question
During a steady climb, the angle of climb depends on
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 110
37. Question
Which statement describes the relationship of the forces acting on an aircraft in a constant-power and constant-airspeed descent?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 110
38. Question
During flight, advancing thrust will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 110
39. Question
If an airplane’s gross weight is 3,250 pounds, what is the load acting on this airplane during a level 60° banked turn?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 110
40. Question
Refer to the diagram below. A positive load factor of 4 at 140 MPH would cause the airplane to
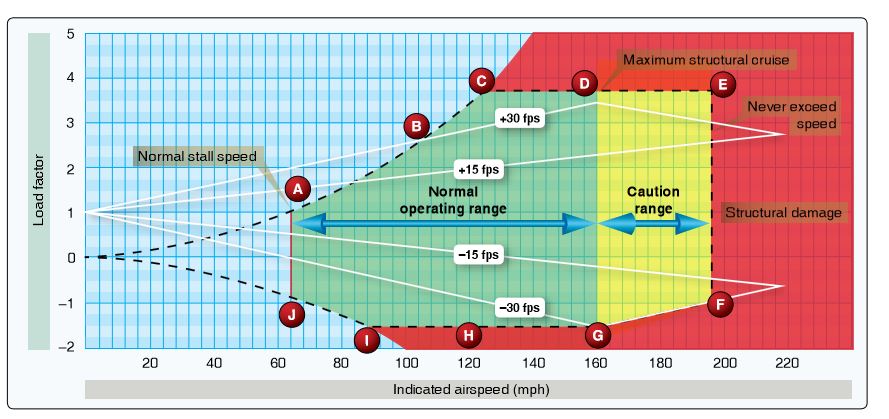 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 110
41. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What load factor would be created if positive 30 feet per second gusts were encountered at 130 MPH?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 110
42. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The horizontal dashed line from point C to point E represents the
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 110
43. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The airspeed indicated by point A is
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 110
44. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The airspeed indicated by point C is
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 110
45. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The airspeed indicated by point E is
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 110
46. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The airspeed indicated by point D is
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 110
47. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What increase in load factor would take place if the angle of bank were increased from 60° to 80°?
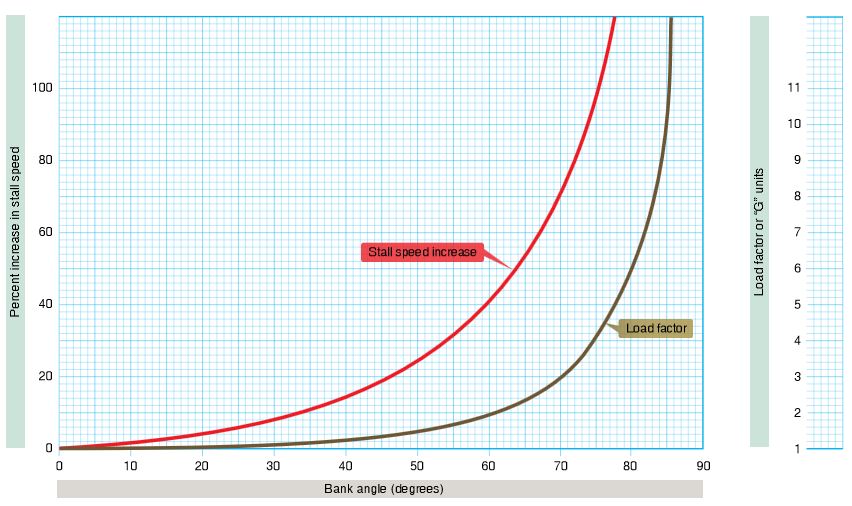 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 110
48. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the stall speed of an airplane under a load factor of 2 if the unaccelerated stall speed is 100 knots?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 110
49. Question
Refer to the diagram below. A 70 percent increase in stalling speed would imply a bank angle of
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 110
50. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the stall speed of an airplane under a load factor of 2 if the unaccelerated stall speed is 100 knots?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 51 of 110
51. Question
Refer to the diagram below. A 70 percent increase in stalling speed would imply a bank angle of
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 110
52. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the stall speed of an airplane in a 30 degree bank turn if the level stall speed is 100 knots?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 53 of 110
53. Question
An airplane has a normal stalling speed of 60MP H but is forced into an accelerated stall at twice t ha t speed. What maximum load factor will result from this maneuver?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 110
54. Question
At a constant velocity in airflow, a high aspect ratio wing will have (in comparison with a low aspect ratio wing)
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 55 of 110
55. Question
The use of a slot in the leading edge of the wing enables an airplane to land at a slower speed because it
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 56 of 110
56. Question
A rectangular wing, as compared to other wing planforms, has a tendency to stall first at the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 57 of 110
57. Question
The angle between the chord line of the wing and the longitudinal axis of the aircraft 1s known as
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 58 of 110
58. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which aircraft has the highest aspect ratio?
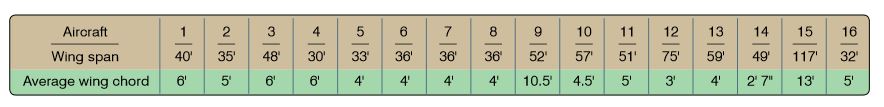 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 59 of 110
59. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which aircraft has the lowest aspect ratio?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 60 of 110
60. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Of aircraft 1, 2, or 3, which has the lowest aspect ratio?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 61 of 110
61. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Consider only aspect ratio (other factors remain constant). Which aircraft will generate greatest lift?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 62 of 110
62. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Consider only aspect ratio (other factors remain constant). Which aircraft will generate greatest drag?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 63 of 110
63. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Consider only aspect ratio (other factors remain constant). Which aircraft will generate the least drag?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 64 of 110
64. Question
Which subsonic planform provides the best lift coefficient?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 65 of 110
65. Question
A line drawn from the leading edge to the trailing edge of an airfoil and equidistant at all points from the upper and lower contours is called the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 66 of 110
66. Question
A sweptwing airplane with weak static directional stability and increased dihedral causes an increase in
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 67 of 110
67. Question
On which wing planform does the stall begin at the wing root and progress outward toward the wingtip?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 68 of 110
68. Question
The purpose of aircraft wing dihedral angle is to
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 69 of 110
69. Question
Aspect ratio of a wing is defined as the ratio of the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 70 of 110
70. Question
A wing with a very high speed ratio (in comparison with a low aspect ratio wing) will have
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 71 of 110
71. Question
The three axes of an aircraft intersect at the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 72 of 110
72. Question
Action of the elevators moves the plane on its
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 73 of 110
73. Question
Aileron deflection moves the airplane about its
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 74 of 110
74. Question
If the pilot applies right rudder to a stable airplane, the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 75 of 110
75. Question
The angle between the chord line of an airfoil and the relative wind is known as the angle of
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 76 of 110
76. Question
The critical angle of attack at which a given aircraft stalls is dependent on the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 77 of 110
77. Question
The angle of attack of a wing directly controls the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 78 of 110
78. Question
As the angle of bank is increased, the vertical component of lift
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 79 of 110
79. Question
How can a pilot increase the rate of turn and decrease the radius at the same time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 80 of 110
80. Question
What action is necessary to make an aircraft turn?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 81 of 110
81. Question
Refer to the diagram below. While rolling into a right turn, if the inclinometer appears as illustrated in A, the HCL and CF vectors would be acting on the aircraft as illustrated in
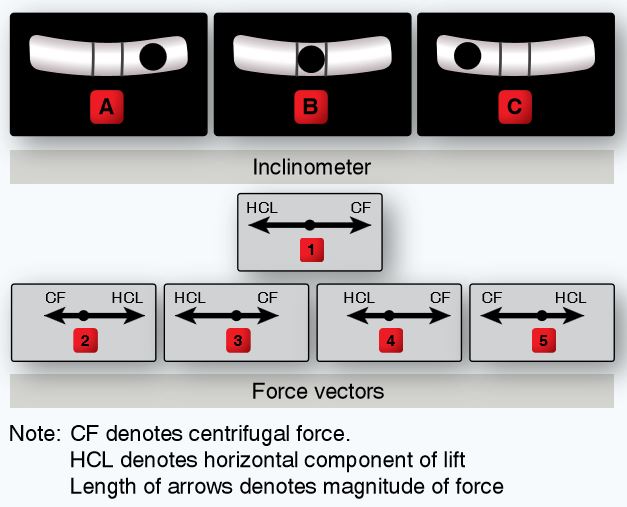 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 82 of 110
82. Question
Refer to the diagram below. While rolling into a right turn, if the inclinometer appears as illustrated in C, the HCL and CF vectors would be acting on the aircraft as illustrated in
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 83 of 110
83. Question
Refer to the diagram below. While rolling out of a left turn, if the inclinometer appears as illustrated in A, the HCL and CF vectors would be acting on the aircraft as illustrated in
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 84 of 110
84. Question
Adverse yaw during a turn entry is caused by
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 85 of 110
85. Question
When rolling out of a steep-banked turn, what causes the lowered aileron to create more drag than when rolling into the turn?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 86 of 110
86. Question
The quality of an aircraft that permits it to be operated easily and to withstand the stresses imposed on it is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 87 of 110
87. Question
The capability of an aircraft to respond to a pilot’s inputs, especially with regard to flightpath and attitude, is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 88 of 110
88. Question
The tendency of an aircraft to develop forces which restore it to its original condition, when disturbed from a condition of steady flight, is known
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 89 of 110
89. Question
The most desirable type of stability for an aircraft to possess is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 90 of 110
90. Question
Which aircraft characteristics contribute to spiral instability?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 91 of 110
91. Question
The tendency of an aircraft to develop forces that further remove the aircraft from its original position, when disturbed from a condition of steady flight, is known as
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 92 of 110
92. Question
If the aircraft’s nose initially tends to return to its original position after the elevator control is pressed forward and released, the aircraft displays
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 93 of 110
93. Question
If the airspeed increases and decreases during longitudinal phugoid oscillations, the aircraft
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 94 of 110
94. Question
If an aircraft has negative dynamic and positive static stability, this will result in
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 95 of 110
95. Question
If the aircraft’s nose initially tends to move farther from its original position after the elevator control is pressed forward and released, the aircraft displays
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 96 of 110
96. Question
If the aircraft’s nose remains in the new position after the elevator control is pressed forward and released, the aircraft displays
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 97 of 110
97. Question
With regard to gyroscopic precession, when a force is applied at a point on the rim of a spinning disc, the resultant force acts in which direction and at what point?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 98 of 110
98. Question
As a result of gyroscopic precession, it can be said that any
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 99 of 110
99. Question
A propeller rotating clockwise, as seen from the rear, creates a spiraling slipstream that tends to rotate the aircraft to the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 100 of 110
100. Question
The angle of attack at which an airplane stalls
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 101 of 110
101. Question
Which action will result in a stall?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 102 of 110
102. Question
Which statement is true relating to the factors which produce stalls?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 103 of 110
103. Question
Which characteristic of a spin is not a characteristic of a steep spiral?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 104 of 110
104. Question
Which statement is true concerning the aerodynamic conditions which occur during a spin entry?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 105 of 110
105. Question
It is possible to fly an aircraft just clear of the ground at a slightly slower airspeed than that required to sustain level flight at higher altitudes. This is the result of
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 106 of 110
106. Question
If the same angle of attack is maintained in ground effect as when out of ground effect, lift will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 107 of 110
107. Question
An airplane is usually affected by ground effect at what height above the surface
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 108 of 110
108. Question
An airplane leaving ground effect will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 109 of 110
109. Question
If severe turbulence is encountered, the aircraft’s airspeed should be reduced to
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 110 of 110
110. Question
Which is the best technique for minimizing the wing-load factor when flying in severe turbulence?
CorrectIncorrect