CFI Airplane Performance
Quiz Summary
0 of 64 questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 64 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 64
1. Question
Density altitude increases with
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 64
2. Question
What would increase the density altitude at a given airport?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 64
3. Question
As altitude increases, the indicated airspeed at which a given airplane stalls in a particular configuration will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 64
4. Question
An altimeter indicates 1,850 feet MSL when set to 30.18. What is the approximate pressure altitude?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 64
5. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the density altitude.
Airport elevation 5,515 ft.
OAT 30°c
Altimeter setting 29.40″ Hg
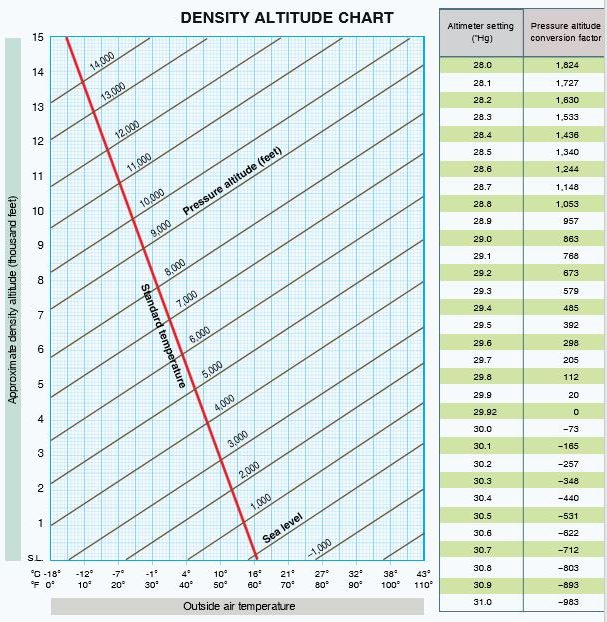 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 64
6. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the density altitude.
Airport elevation 3,795 ft
OAT 24°c
Altimeter setting 29.70″ Hg
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 64
7. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the density altitude.
Airport elevation 3,450 feet
OAT 35 degrees C
Altimeter setting 30.40″ Hg
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 64
8. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the effect of a temperature increase from 30 to 50°F on the density altitude if the pressure altitude remains at 3,000 feet MSL?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 64
9. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the pressure altitude at an airport that is 3,563 feet MSL with an altimeter setting of 29.96.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 64
10. Question
What is pressure altitude?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 64
11. Question
Under what condition is indicated altitude the same as true altitude?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 64
12. Question
What is true altitude?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 64
13. Question
What is absolute altitude?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 64
14. Question
Density altitude may be determined by correcting
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 64
15. Question
What effect does high density altitude, as compared to low density altitude, have on propeller efficiency and why?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 64
16. Question
Which combination of atmospheric conditions will reduce aircraft takeoff and climb performance?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 64
17. Question
If the outside air temperature (OAT) at a given altitude is warmer than standard, the density altitude is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 64
18. Question
What effect does high density altitude have on aircraft performance?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 64
19. Question
If the atmospheric pressure and temperature remain the same, how would an increase in humidity affect takeoff performance?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 64
20. Question
Which statement is true regarding takeoff performance with high density altitude conditions?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 64
21. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the ground roll required for takeoff.
Temperature 24 degrees C
Pressure altitude 2,500 feet
Weight 2,400 lb.
Headwind 25 kts.
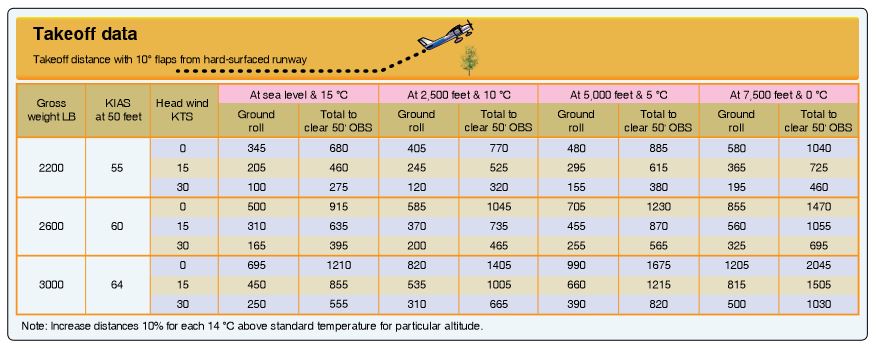 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 64
22. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the ground roll required for takeoff.
Temperature 25 degrees C
Pressure Altitude 2,000 ft.
Weight 2,200 lb.
Headwind 15 knots
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 64
23. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the takeoff distance required to clear a 50-foot obstacle.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 64
24. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the takeoff distance required to clear a 50-foot obstacle.
Temperature 3 degrees C
Pressure Altitude 6,000 ft.
Weight 3,000 lb.
Headwind 15 knots
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 64
25. Question
How does increased weight affect the takeoff distance of an airplane?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 64
26. Question
What effect does an uphill runway slope have upon takeoff performance?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 64
27. Question
When density altitude is beyond capability as indicated on the performance chart,
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 64
28. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the approximate total distance required to clear a 50-foot obstacle.
Temperature 20 degrees C
Pressure altitude 1,000 ft.
Surface sod
Weight 5,300 lb.
Wind 15 kts. headwind
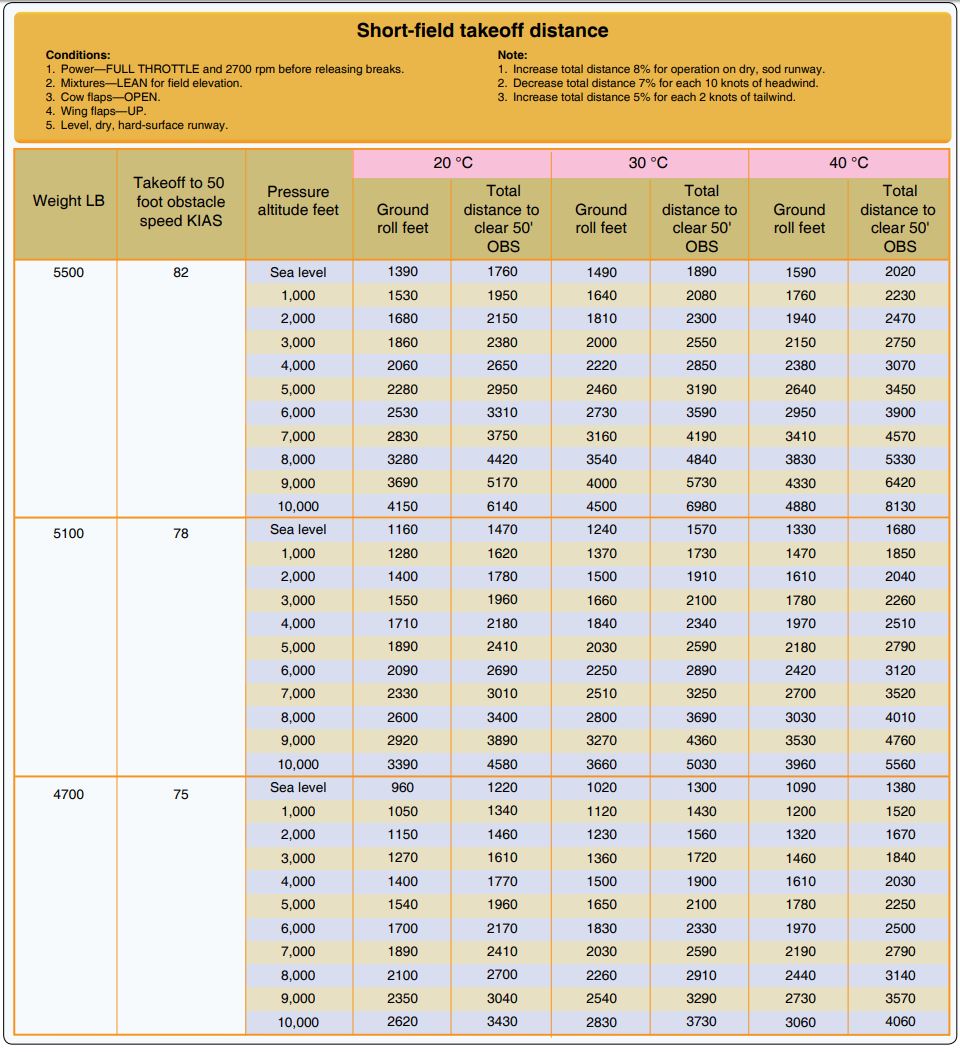 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 64
29. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the approximate total distance required to clear a 50-foot obstacle.
Temperature 35 degrees C
Pressure altitude 3,000 ft.
Surface sod
Weight 5,100 lb.
Wind 20 kts. headwind
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 64
30. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the approximate total distance required to clear a 50-foot obstacle.

Temperature 25 degrees C
Pressure altitude 2,500 ft.
Surface asphalt
Weight 5,500 lb.
Wind 2 kts. tailwindCorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 64
31. Question
Refer to the diagram below.. The indicated airspeed that would give the greatest gain in altitude in a unit of time at 3,200 feet is determined to be
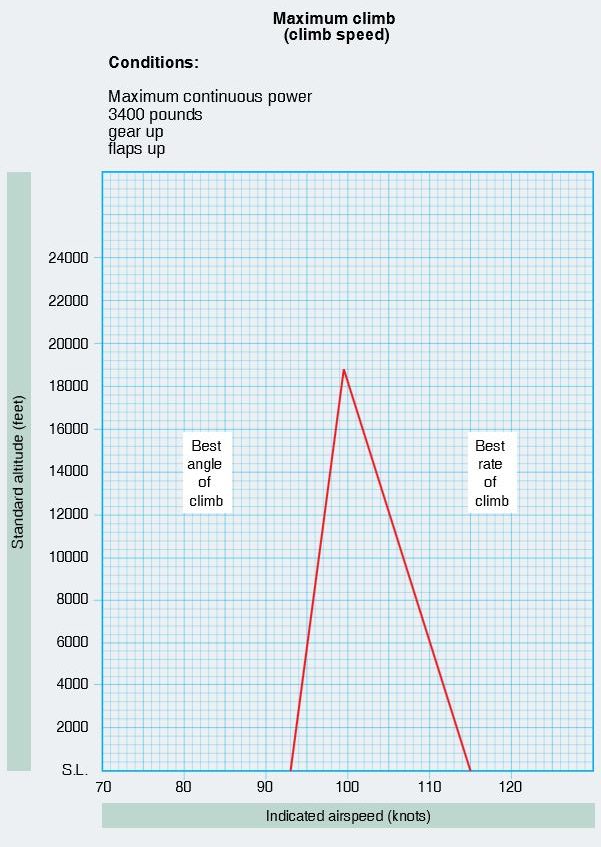 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 64
32. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What indicated airspeed at 3,000 feet would result in the greatest increase in altitude for a given distance?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 64
33. Question
Refer to the diagram below. To maintain the best rate of climb, the indicated speed should be
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 64
34. Question
An aircraft is flying at a constant power setting and constant indicated altitude. If the outside air temperature (OAT) decreases, true airspeed will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 64
35. Question
An aircraft is flying at a constant power setting and constant indicated altitude. If the outside air temperature (OAT) increases, true airspeed will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 64
36. Question
As density altitude increases, which will occur if a constant indicated airspeed is maintained in a no-wind condition?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 64
37. Question
In a propeller-driven airplane, maximum range occurs at
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 64
38. Question
The critical engine on most light multiengine airplanes with clockwise rotating propellers is the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 64
39. Question
On a multiengine airplane with engines which rotate clockwise, the critical engine is the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 64
40. Question
What is the significance of the blue radial line on the airspeed indicator of a light multiengine airplane and when is it to be used? It indicates the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 64
41. Question
On a multiengine airplane, where the propellers rotate in the same direction, why is the loss of power on one engine more critical than the loss of power on the other engine?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 64
42. Question
For an airplane with reciprocating, nonturbo charged engines, VMc
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 64
43. Question
When one engine fails on a twin-engine airplane, the resulting performance loss
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 64
44. Question
Which is true regarding the operation of a multiengine airplane with one engine inoperative?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 64
45. Question
In a twin-engine airplane, the single-engine service ceiling is the maximum density altitude at which VvsE will produce
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 64
46. Question
When operating a light multiengine airplane at VMc, the pilot should expect performance to be sufficient to maintain
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 64
47. Question
Which condition causes VMc to be the highest?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 64
48. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the approximate glide distance?
Height above terrain 7,500 ft.
Headwind 30 knots
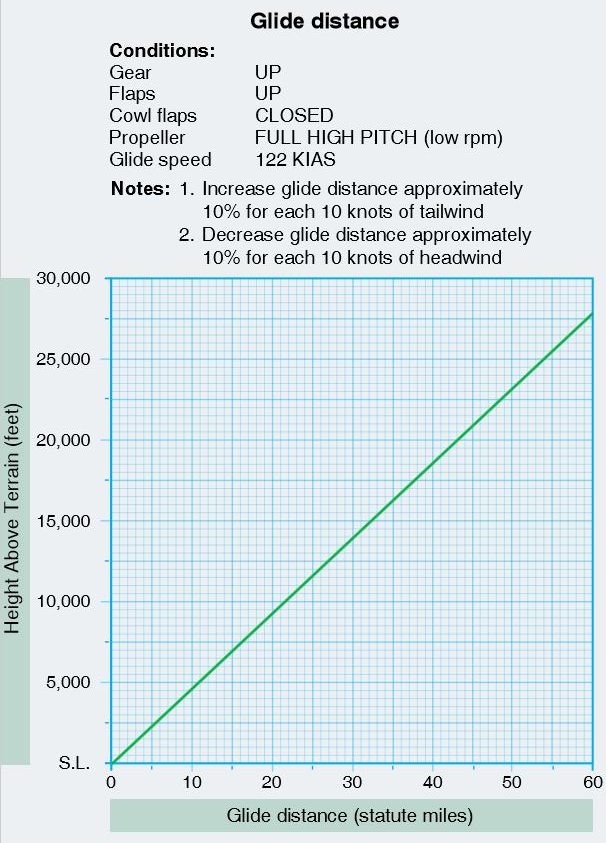 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 64
49. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the approximate glide distance?
Height above terrain 10,500 feet
Tailwind 20 knots
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 64
50. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the approximate glide distance?
Height above terrain 5,500 feet
Tailwind 10 knots
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 51 of 64
51. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What would be the indicated stall speed in a 60° banked turn with the gear and flaps up?
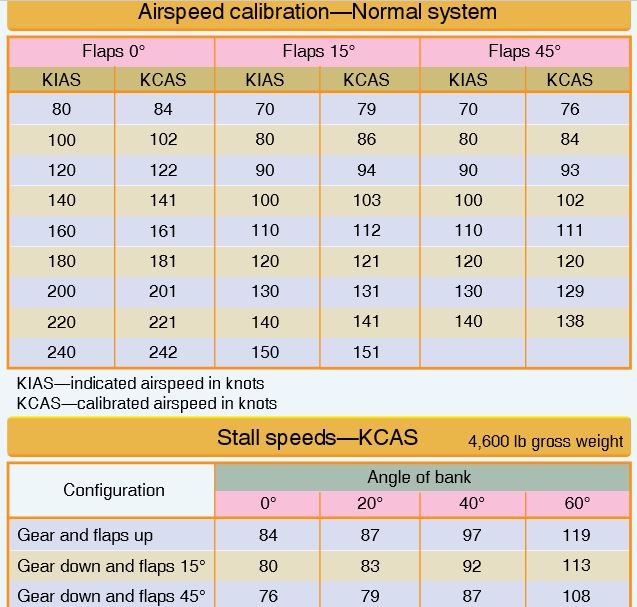 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 64
52. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What would be the indicated stall speed in a 30° banked turn with the gear down and flaps set at 15°?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 53 of 64
53. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What would be the indicated stall speed during a 40° banked turn with the gear down and flaps set at 45°?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 64
54. Question
What can a pilot expect when landing at an airport located in the mountains?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 55 of 64
55. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the total landing distance over a 50-foot obstacle?
Temperature 15 degrees C
Pressure altitude 4,000 feet
Weight 3,000 pounds
Headwind 22 knots
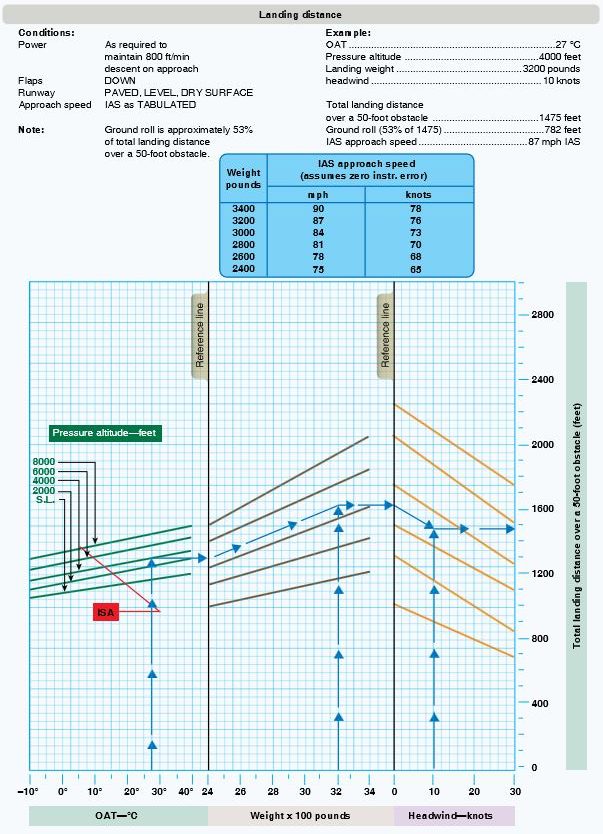 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 56 of 64
56. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the approximate groundroll.
Temperature 33 degrees C
Pressure altitude 6,000 feet
Weight 2.800 pounds
Headwind 14 knots
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 57 of 64
57. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the total landing distance over a 50-foot obstacle?
Temperature 35 degrees
Pressure altitude 2,000 feet
Weight 3,400 pounds
Headwind 10 knots
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 58 of 64
58. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the approximate crosswind component.
Landing Rwy 30
Wind 020 degrees at 15 knots
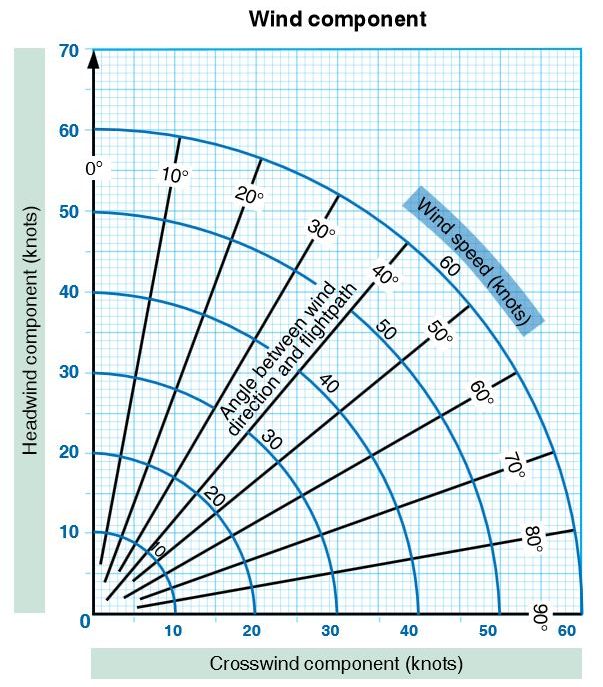 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 59 of 64
59. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the approximate crosswind component.
Landing Rwy 03
Wind 060 degrees at 35 knots
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 60 of 64
60. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the crosswind component for a landing on Runway 18 if the tower reports the wind as 220 degrees at 25 knots?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 61 of 64
61. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Determine the approximate crosswind component.
Landing Rwy 22
Wind 260 degrees at 23 knots CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 62 of 64
62. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Using a maximum demonstrated crosswind component equal to 0.2 Vso , what is a pilot able to determine?
Vso 70 knots
Landing Rwy 35
Wind 300 degrees at 20 knots CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 63 of 64
63. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Using a maximum demonstrated crosswind component equal to 0.2 Vso , what is a pilot able to determine?
Vso 60 knots
Landing Rwy 12
Wind 150 degrees at 20 knots
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 64 of 64
64. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Using a maximum demonstrated crosswind component equal to 0.2 Vso , what is a pilot able to determine?
Vso 65 knots
Landing Rwy 17
Wind 200 degrees at 30 knots
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect