CFI – Navigation
Quiz Summary
0 of 92 questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 92 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 92
1. Question
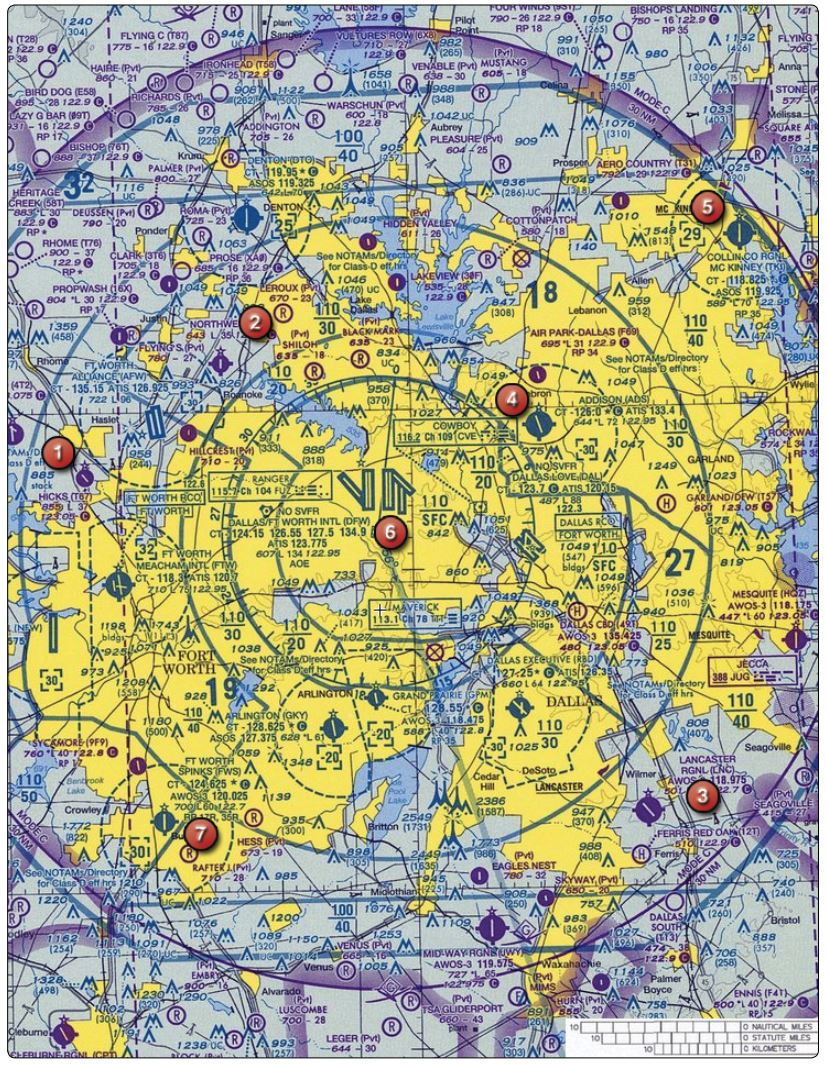
Refer to the diagram below. Where does the floor of positively controlled ATC airspace begin over Hicks Airport – area 1?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 92
2. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The airspace overlying Addison Airport, area 4, is classified as
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 92
3. Question
Refer to the diagram below. An aircraft takes off from Hicks Airport , area 1, and flies northeast towards Northwest Airport, area 2. What maximum elevation figure would assure obstruction clearance during the flight?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 92
4. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Where does the floor of controlled airspace begin over Ft. Worth Meacham, area 1?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 92
5. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Select the correct statement concerning the obstruction 7 SM west of McKinney Airport, area 5.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 92
6. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Select the correct statement concerning special VFR operations at Addison Airport, area 4.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 92
7. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What altitude should be selected to avoid operating in Class B airspace on a flight from Northwest Airport, area 2, to McKinney Airport, area 5.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 92
8. Question
Refer to the diagram below. When, if ever, are two-way radio communications required while en route from Lancaster Airport, area 3, direct to McKinney Airport, area 5, at 2,700 feet MSL?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 92
9. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Select the correct statement concerning the Maverick VOR, area 6.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 92
10. Question
When converting from true course to magnetic heading, a pilot should
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 92
11. Question
What are the visibility and cloud clearance requirements at an airport in Class G airspace when conducting takeoffs and landings at night?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 92
12. Question
The angular difference between true north and magnetic north is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 92
13. Question
Refer to the diagram below. An aircraft takes off from Hicks Airport, area 1, and flies northeast towards Northwest Airport, area 2. What maximum altitude could be flown to remain under the Class B airspace?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 92
14. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What minimum avionics equipment is necessary to operate in the airspace up to 3,000 feet MSL over Northwest Airport, area 2?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 92
15. Question
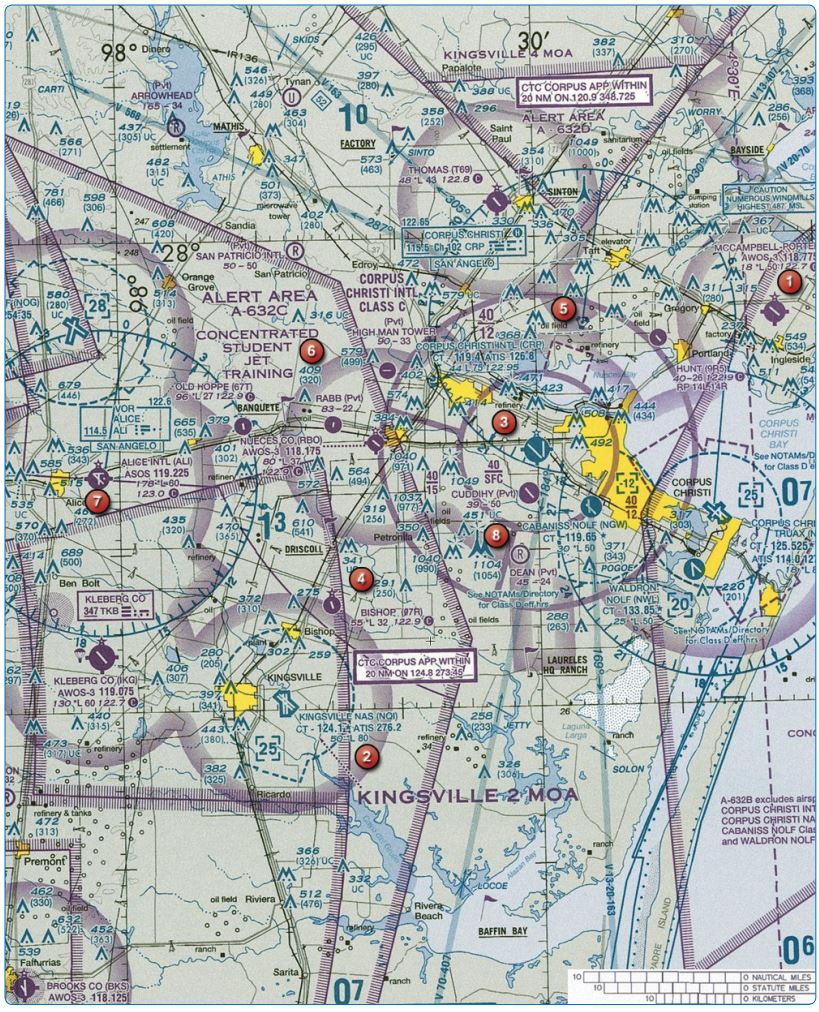
Refer to the diagram below. Where does the floor of controlled airspace begin over McCampbell Airport, area 1?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 92
16. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What are the visibility and cloud clearance requirements in an airplane at night when conducting takeoffs and landings at McCampbell Airport , area 1?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 92
17. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The controlled airspace located at the Corpus Christi VORTAC, area 5, begins at
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 92
18. Question
Refer to the diagram below. When are two-way radio communications required on a flight from Bishop Airport, area 4, to McCampbell Airport, area 1, at an altitude of 2,000 feet MSL?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 92
19. Question
Refer to the diagram below. While on a flight from Alice Airport, area 7, to McCampbell Airport, area 1, at 5,500 feet MSL, when, if ever, is a transponder required?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 92
20. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Assuming owner permission, what minimum avionics equipment is required for operation into Cuddihy Airport, area 8?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 92
21. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The airspace beginning at the surface overlying NAS Kingsville, area 2, is
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 92
22. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the elevation of the Thomas-T69 Airport, area 5?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 92
23. Question
When converting from magnetic course to true course, a pilot should
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 92
24. Question
When converting from true heading to true course, a pilot should
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 92
25. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What are the requirements for operating in the alert area, area 6, just west of Corpus Christi International Airport, area 3?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 92
26. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the elevation of the top of the obstruction located approximately 3 NM northwest of McCampbell Airport, area 1?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 92
27. Question
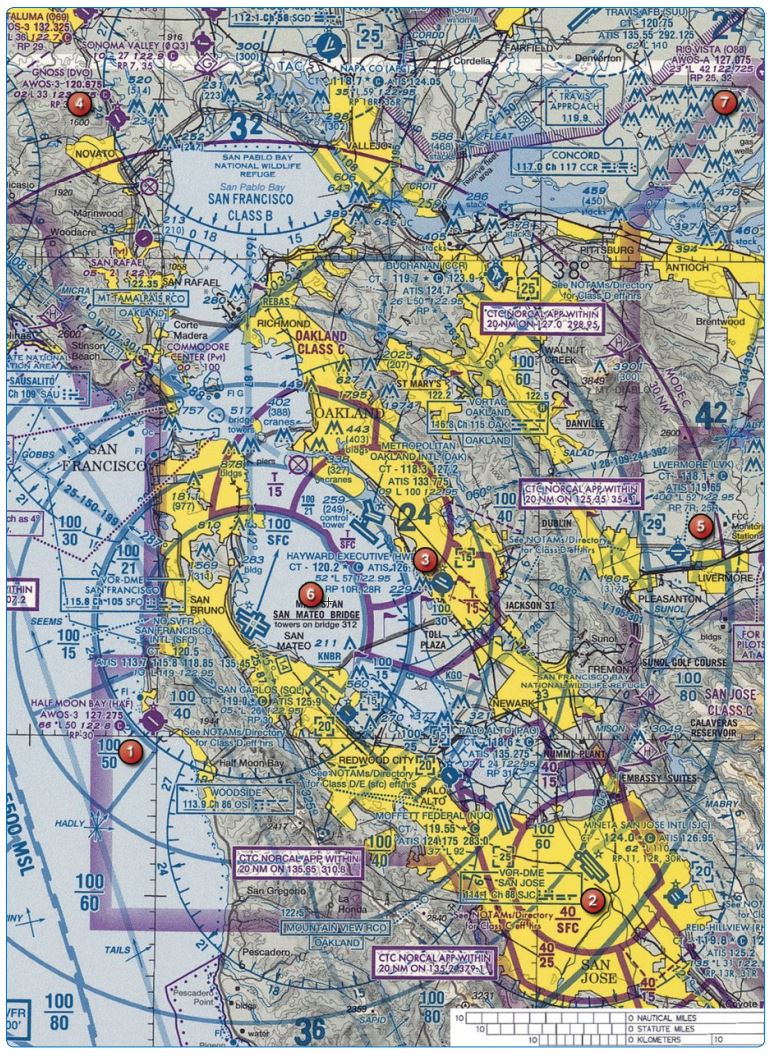
Refer to the diagram below. An aircraft takes off from Gnoss Airport, area 4, and flies eastward to Rio Vista Airport , area 7). What maximum elevation figure would assure obstruction clearance during the flight?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 92
28. Question
Refer to the diagram below. When are two way radio communications required on a flight from Gnoss Airport- DVO, Area 4, to Livermore Airport-LVK, Area 5, at an altitude of 3,500 ft. AGL? When entering
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 92
29. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Where does the floor of controlled airspace begin over Half Moon Bay Airport, area 1?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 92
30. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the height of the Class D airspace over Livermore Airport , area 5?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 92
31. Question
Refer to the diagram below. While on a flight from Livermore Airport, area 5, to Gnoss Airport, area 4, you contact San Francisco Approach Control and request clearance through the Class B airspace. The controller states “Radar contact, standby.” What are you authorized to do?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 92
32. Question
Refer to the diagram below. At what altitude does the Class B airspace begin over Hayward Airport, area 3?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 92
33. Question
Refer to the diagram below, At what altitude does the Class D airspace terminate over Hayward Airport, area 3?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 92
34. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The airport immediately northwest of Metropolitan Oakland International-OAK, area 3, is a
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 92
35. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What is the ceiling of the Class C airspace surrounding San Jose International Airport, area 2?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 92
36. Question
Refer to the diagram below. What does the figure 24, area 6, indicate?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 92
37. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The minimum avionics equipment necessary to operate in the airspace above 10,000 feet MSL over San Francisco International Airport, area 6, is
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 92
38. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The minimum avionics equipment necessary to operate in the airspace above 8,000 feet MSL over San Francisco International Airport, area 6, is
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 92
39. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The area around Sonoma Valley-OQ3, area 4, is a
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 92
40. Question
Which statement about longitude and latitude is true?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 92
41. Question
When diverting to an alternate airport because of an emergency, pilots should
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 92
42. Question
When planning a distance flight, true course measurements on a Sectional Aeronautical Chart should be made at a meridian near the midpoint of the course because the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 92
43. Question
GIVEN:
Departure path straight out
Takeoff time 1030 DST
Winds during climb 180° at 30 kts
True course during climb 60°
Airport elevation 1500 feet
True airspeed 125 kts.
Rate of climb 500 ft/minCorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 92
44. Question
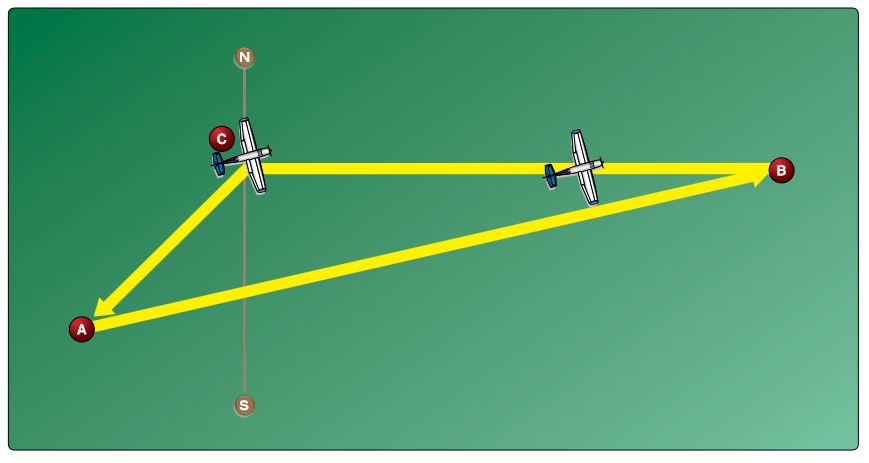
Refer to the diagram below. The line from point A to point B of the wind triangle represents
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 92
45. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The line from point C to point B of the wind triangle represents
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 92
46. Question
Refer to the diagram below. The line from point C to point A of the wind triangle represents
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 92
47. Question
GIVEN:
Usable fuel at takeoff 36 gal.
Fuel consumption rate 12.4 gal/hr 140 kts
Constant groundspeed 140 kts.
Flight time since takeoff 48 min.According to 14 CFR Part 91, how much farther can an airplane be flown under day VFR?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 92
48. Question
On a cross-country flight, point A is crossed at 1500 hours and the plan is to reach point B at 1530 hours. Use the following information to determine the indicated airspeed required to reach point B on schedule.
Distance between A and B 70 NM
Forecast wind 310° at 15 kts
Pressure altitude 8,000 ft
Ambient temperature – 10°C
True course 270°
The required indicated airspeed would be approximatelyCorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 92
49. Question
GIVEN:
Usable fuel at takeoff 40 gal.
Fuel consumption rate 12.2 gal/hr
Constant groundspeed 120 kts
Flight time since takeoff 1 hour 30 minutes
According to 14 CFR Part 91, how much farther can an airplane be flown under night VFR?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 92
50. Question
If fuel consumption is 15.3 gallons per hour and groundspeed is 167 knots, how much fuel is required for an aircraft to travel 620 NM
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 51 of 92
51. Question
If an aircraft is consuming 91 pounds of fuel per hour and groundspeed is 168 knots, how much fuel is required to travel 457 NM?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 92
52. Question
GIVEN:
Departure path Straight out
Takeoff time 1435Z
Winds during climb 175° at 25 kts
True course during climb 155°
Airport elevation 2,000 feet
True airspeed 130 knots
Rate of climb 500 ft/minWhat would be the distance and time upon reaching 8,000 feet MSL?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 53 of 92
53. Question
GIVEN:
Distance 300 NM
True course 260 degrees
Wind 245 degrees at 45 knots
True airspeed 119 knots
Rate of fuel/consumption 12.7 gallons/hour
What would be the approximate groundspeed and amount of fuel consumed?What would be the approximate groundspeed and amount of fuel consumed?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 92
54. Question
GIVEN:
Distance 200 NM
True course 320°
Wind 215° at 25 kts
True airspeed 116 kts
Rate of fuel consumption 19 gal/hr
What would be the approximate groundspeed and amount of fuel consumed?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 55 of 92
55. Question
GIVEN:
Usable fuel at takeoff 36 gal
Fuel consumption rate 12.4 gal/hr
Constant groundspeed 140 kts
Flight time since takeoff 48 minAccording to 14 CFR Part 91, how much farther can an airplane be flown under night VFR?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 56 of 92
56. Question
How far will an aircraft travel in 2-1/2 minutes with a groundspeed of 98 knots?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 57 of 92
57. Question
How far will an aircraft travel in 3-1/2 minutes if its groundspeed is 165 knots?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 58 of 92
58. Question
How far will an aircraft travel in 3-1/2 minutes if its groundspeed is 65 knots?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 59 of 92
59. Question
How far will an aircraft travel in 3-1/2 minutes if its groundspeed is 55 knots?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 60 of 92
60. Question
On a cross-country flight, point X is crossed at 1015 and arrival at point Y is expected at 1025. Use the following information to determine the indicated airspeed required to reach point Y on schedule
Distance between X and Y 27 NM
Forecast wind 240° at 30 kts
Pressure altitude 5,500 ft
Ambient temperature +05°C
True course 100°The required indicated airspeed would be approximately
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 61 of 92
61. Question
On a cross-country flight, point X is crossed at 1550 and the plan is to reach point Y at 1620. Use the following information to determine the indicated airspeed required to reach point Y on schedule.
Distance between X and Y 70 NM
Forecast wind 115 degrees at 25 knots
Pressure altitude 9,000 ft.
Ambient temperature -05 degrees C
True course 088 degrees
The required indicated airspeed would be approximately115° at 25 kts
9,000 ft
-05°C 088°
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 62 of 92
62. Question
GIVEN:
True course 258 degrees
Variation 10 degrees E
Indicated airspeed 142 knots
Ambient temperature +05 degrees C
Pressure altitude 6,500 feet
Forecast wind 350 degrees at 30 knotsUnder these conditions, the magnetic heading and groundspeed would be approximately
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 63 of 92
63. Question
GIVEN:
True course 330°
Variation 15 degrees E
Indicated airspeed 160 knots
Ambient temperature -10 degrees C
Pressure altitude 4,500 feet
Forecast wind 090 degrees at 25 knotsUnder these conditions, the magnetic heading and groundspeed would be approximately
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 64 of 92
64. Question
GIVEN:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 65 of 92
65. Question
On a cross-country flight, point X is crossed at 1015 local. What is your expected arrival time at point Y? Use the following information to determine your ETA.
Distance between X and Y = 32 NMForecast wind = 240° at 25 kts
Pressure altitude = 5,500 ft
Ambient temperature = +05°
True course = 100°
The indicated airspeed is 110 knotsCorrectIncorrect -
Question 66 of 92
66. Question
After 141 miles are flown from the departure point, the aircraft’s position is located 11 miles off course. If 71 miles remain to be flown, what approximate total correction should be made to converge on the destination?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 67 of 92
67. Question
After 150 miles are flown from the departure point, the aircraft’s position is located 8 miles off course. If 160 miles remain to be flown, what approximate total correction should be made to converge on the destination?
destination?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 68 of 92
68. Question
After 240 miles are flown from the departure point, the aircraft’s position is located 25 miles off course. If 100 miles remain to be flown, what approximate total correction should be made to converge on the destination?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 69 of 92
69. Question
If a true heading of 135° results in a ground track of 130° and a true airspeed of 135 knots results in a groundspeed of 140 knots, the wind would be from
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 70 of 92
70. Question
If a true heading of 350° results in a ground track of 335° and a true airspeed of 140 knots results in a groundspeed of 115 knots, the wind would be from
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 71 of 92
71. Question
If a true heading of 230 degrees results in a ground track of 250 degrees and a true airspeed of 160 knots results in a groundspeed of 175 knots, the wind wind would be from
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 72 of 92
72. Question
Which distance is commonly displayed by a DME indicator?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 73 of 92
73. Question
Which DME indication should you receive when you are directly over a VORTAC site at approximately 6,000 feet AGL
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 74 of 92
74. Question
Which statement is true concerning the operation of DME
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 75 of 92
75. Question
The slant-range error of a DME is greatest at
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 76 of 92
76. Question
A particular VORTAC station is undergoing routine maintenance. This is evidenced by
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 77 of 92
77. Question
When using a VOT to check the accuracy of a VOR receiver, with the CDI centered, what should the OBS indicate if no error exists?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 78 of 92
78. Question
The normal usable range of an L class VOR below 18,000 feet is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 79 of 92
79. Question
The normal usable range of a T class VOR below 12,000 feet is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 80 of 92
80. Question
While maintaining a magnetic heading of 060° and a true airspeed of 130 knots, the 150° radial of a VOR is crossed at 1137 and the 140° radial at 1145. The approximate time and distance to the station would be
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 81 of 92
81. Question
While maintaining a magnetic heading of 180° and a true airspeed of 130 knots, the 270° radial of a VOR is crossed at 1037 and the 260° radial at 1042. The approximate time and distance to the station would be
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 82 of 92
82. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Refer to the diagram below. At which aircraft position(s) would you receive OMNI indication V?
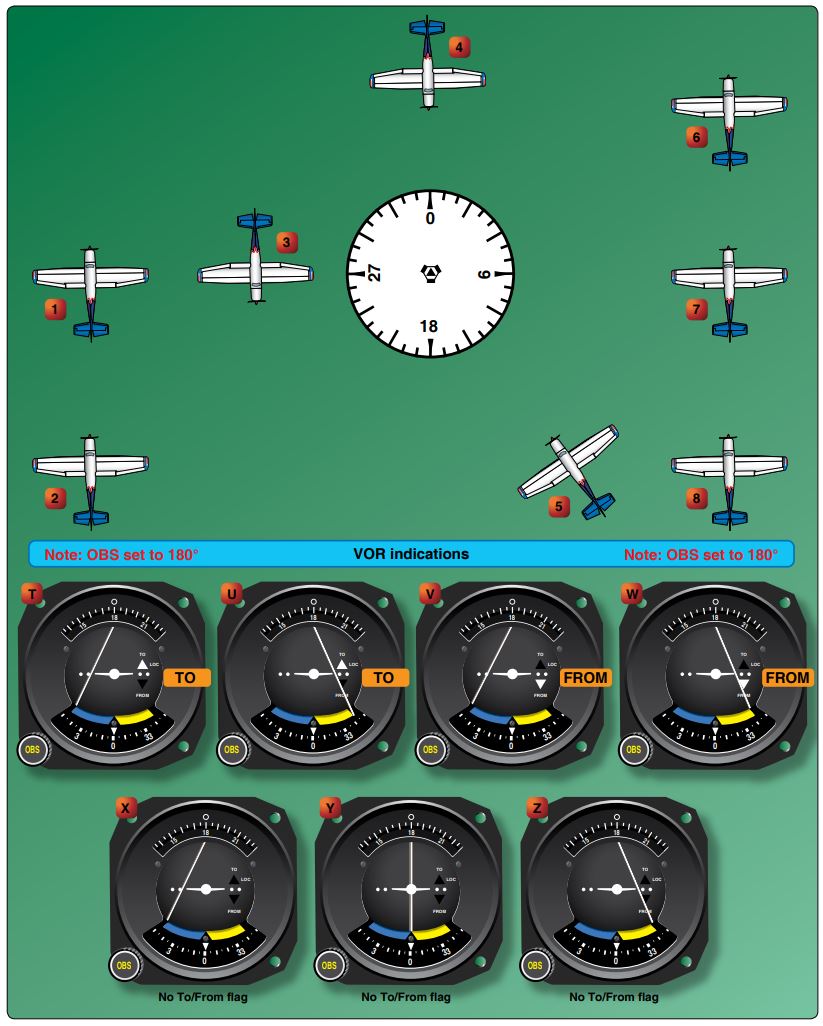 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 83 of 92
83. Question
Refer to the diagram below. At which aircraft position(s) would you receive OMNI indication X?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 84 of 92
84. Question
Refer to the diagram below. At which aircraft position(s) would you receive OMNI indication U?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 85 of 92
85. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which OMNI indication would you receive for aircraft 8?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 86 of 92
86. Question
Refer to the diagram below. Which OMNI indications would you receive for aircraft 5 and 7?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 87 of 92
87. Question
The three individual navigation services provided by a VORTAC facility are
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 88 of 92
88. Question
The primary purpose of the direct-to button is to
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 89 of 92
89. Question
Which button/feature provides information on the closest airport at any given time?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 90 of 92
90. Question
Effective navigation by means of GPS includes
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 91 of 92
91. Question
Why should pilots understand how to cancel entries made on a GPS?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 92 of 92
92. Question
Reliance on GPS units
CorrectIncorrect