Commercial – Chapter 1 – Airplanes and Aerodynamics
Quiz Summary
0 of 87 questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 87 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 87
1. Question
One of the main functions of flaps during the approach and landing is to
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 87
2. Question
Which is true regarding the use of flaps during level turns?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 87
3. Question
Some aircraft are fitted with wing spoilers to decrease
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 87
4. Question
An aircraft airfoil is designed to produce lift resulting from a difference in the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 87
5. Question
A rectangular wing, as compared to other wing planforms, has a tendency to stall first at the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 87
6. Question
The angle of attack of a wing directly controls the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 87
7. Question
Frost covering the upper surface of an airplane wing usually will cause
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 87
8. Question
By changing the angle of attack of a wing, the pilot can control the airplane’s
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 87
9. Question
When a pilot increases the angle of attack on a symmetrical airfoil, the center of pressure will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 87
10. Question
The critical angle of attack is exceeded when
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 87
11. Question
The angle of attack at which a wing stalls remains constant regardless of
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 87
12. Question
The design maneuvering speed is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 87
13. Question
The need to slow an aircraft below Va is brought about by the following weather phenomenon.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 87
14. Question
Stall speed is affected by
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 87
15. Question
An airplane will stall at the same
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 87
16. Question
Refer to figure 2 below. Select the correct statement regarding stall speeds.
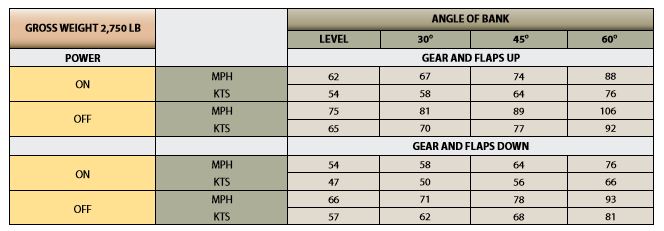 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 17 of 87
17. Question
Refer to figure 2 below. Select the correct statement regarding stall speeds. The airplane will stall
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 18 of 87
18. Question
A stall will occur
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 19 of 87
19. Question
Refer to figure 3 below. Use the diagram to determine the critical angle of attack
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 87
20. Question
In a rapid recovery from a dive, the effects of load factor would cause the stall speed to
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 21 of 87
21. Question
The stalling speed of an airplane is most affected by
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 22 of 87
22. Question
Recovery from a stall in any airplane becomes more difficult when its
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 23 of 87
23. Question
A left side slip is used to counteract a crosswind drift during the final approach for landing. An over-the top spin would most likely occur if the controls were used in which of the following ways? Holding the stick
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 24 of 87
24. Question
In small airplanes, normal recovery from spins may become difficult if the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 25 of 87
25. Question
Which statement is true relative to changing angle of attack?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 87
26. Question
To generate the same amount of lift as altitude is increased, an airplane must be flown at
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 87
27. Question
A pilot who intends to maintain level flight must coordinate the angle of attack and
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 87
28. Question
As the angle of bank is increased, the vertical component of lift
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 87
29. Question
Which is true regarding the forces acting on an aircraft in a steady-state descent? The sum of all
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 87
30. Question
During the transition from straight-and-level flight to a climb, the angle of attack is increased and lift
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 87
31. Question
Which is true regarding the force of lift in steady, unaccelerated flight?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 87
32. Question
What changes in airplane longitudinal control must be made to maintain altitude while the airspeed is being decreased?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 87
33. Question
In theory, if the airspeed of an airplane is doubled while in level flight, parasite drag will become
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 87
34. Question
As airspeed decreases in level flight below that speed for maximum lift/drag ratio, total drag of an airplane
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 87
35. Question
If airspeed remains constant, but the air density increases, what will be the effect on both lift and drag?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 87
36. Question
Refer to figure 1 below. At an airspeed represented by point B, in steady flight, the pilot can expect to obtain the airplane’s maximum
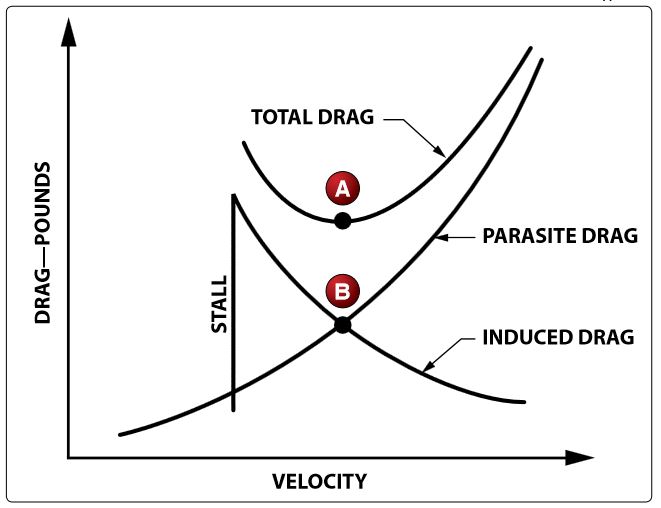 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 87
37. Question
Refer to figure 1 below. At the airspeed represented by point A, in steady flight, the airplane will
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 87
38. Question
What performance is characteristic of flight at maximum lift/drag ratio in a propeller-driven airplane? Maximum
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 87
39. Question
In theory, if the angle of attack and other factors remain constant and the airspeed is doubled, the lift produced at the higher speed will be
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 87
40. Question
An aircraft wing is designed to produce lift resulting from a difference in the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 87
41. Question
To hold an airplane in level flight at airspeeds from very slow to very fast, a pilot must coordinate thrust and
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 87
42. Question
Lift on a wing is most properly defined as the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 87
43. Question
In theory, if the airspeed of an aircraft is cut in half while in level flight, parasite drag will become
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 87
44. Question
Refer to figure 3 below. If an airplane glides at an angle of attack of 10 degrees, how much altitude will it lose in 1 mile?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 87
45. Question
Refer to figure 3 below. How much altitude will this airplane lose in 3 statute miles of gliding at an angle of attack of 8 degrees?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 87
46. Question
Refer to figure 3 below. The L/D ratio at a 2 degree angle of attack is approximately the same as the L/D ratio for a
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 87
47. Question
On a wing, the force of lift acts perpendicular to and the force of drag acts parallel to the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 87
48. Question
Which statement is true regarding the opposing forces acting on an airplane in steady-state level flight?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 87
49. Question
Both lift and drag would be increased when which of these devices are extended?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 87
50. Question
Refer to figure 3A below. As you are flying with a headwind from the coastline inland toward your destination airport, your aircraft has engine failure. You would expect your glide path to be
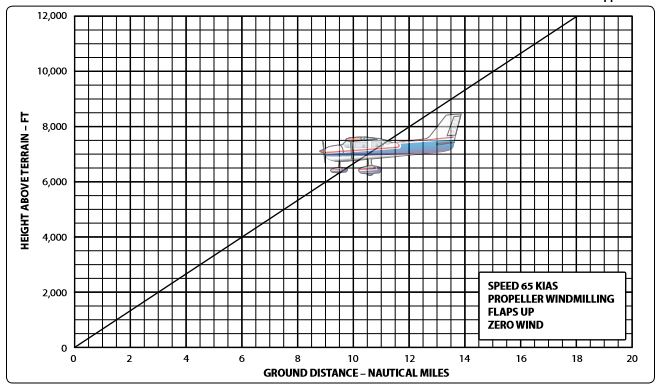 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 51 of 87
51. Question
Refer to figure 3A below. At an altitude of 2,000 feet AGL, how far would you expect to glide?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 52 of 87
52. Question
An airplane leaving ground effect will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 53 of 87
53. Question
To produce the same lift while in ground effect as when out of ground effect, the airplane requires
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 54 of 87
54. Question
If the same angle of attack is maintained in ground effect as when out of ground effect, lift will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 55 of 87
55. Question
Longitudinal stability involves the motion of the airplane controlled by its
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 56 of 87
56. Question
Longitudinal dynamic instability in an airplane can be identified by
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 57 of 87
57. Question
If the airplane attitude remains in a new position after the elevator control is pressed forward and released, the airplane displays
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 58 of 87
58. Question
If the airplane attitude initially tends to return to its original position after the elevator control is pressed forward and released, the airplane displays
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 59 of 87
59. Question
If an airplane is loaded to the rear of its CG range, it will tend to be unstable about its
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 60 of 87
60. Question
If airspeed is increased during a level turn, what action would be necessary to maintain altitude? The angle of attack
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 61 of 87
61. Question
If a standard rate turn is maintained, how long would it take to turn 360 degrees?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 62 of 87
62. Question
While holding the angle of bank constant in a level turn, if the rate of turn is varied the load factor would
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 63 of 87
63. Question
Which is correct with respect to rate and radius of turn for an airplane flown in a coordinated turn at a constant altitude?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 64 of 87
64. Question
To increase the rate of turn and at the same time decrease the radius, a pilot should
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 65 of 87
65. Question
While maintaining a constant angle of bank and altitude in a coordinated turn, an increase in airspeed will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 66 of 87
66. Question
Why is it necessary to increase back elevator pressure to maintain altitude during a turn? To compensate for the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 67 of 87
67. Question
To maintain altitude during a turn, the angle of attack must be increased to compensate for the decrease in the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 68 of 87
68. Question
The ratio between the total airload imposed on the wing and the gross weight of an aircraft in flight is known as
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 69 of 87
69. Question
Load factor is the lift generated by the wings of an aircraft at any given time.
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 70 of 87
70. Question
For a given angle of bank, in any airplane, the load factor imposed in a coordinated constant-altitude turn
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 71 of 87
71. Question
Airplane wing loading during a level coordinated turn in smooth air depends upon the
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 72 of 87
72. Question
The load factor for an airplane in a 60 degree banked turn is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 73 of 87
73. Question
A load factor of 1.2 means the total load on an aircraft’s structure is 1.2 times its
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 74 of 87
74. Question
If an aircraft with a gross weight of 2,000 pounds was subjected to a 60° constant-altitude bank, the total load would be
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 75 of 87
75. Question
If the airspeed is increased from 90 knots to 135 knots during a level 60° banked turn, the load factor will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 76 of 87
76. Question
If the airspeed is decreased from 98 knots to 85 knots during a coordinated level 45° banked turn, the load factor will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 77 of 87
77. Question
Refer to figure 4 below. What increase in load factor would take lace if the angle of bank were increased from 60 degrees to 80 degrees.
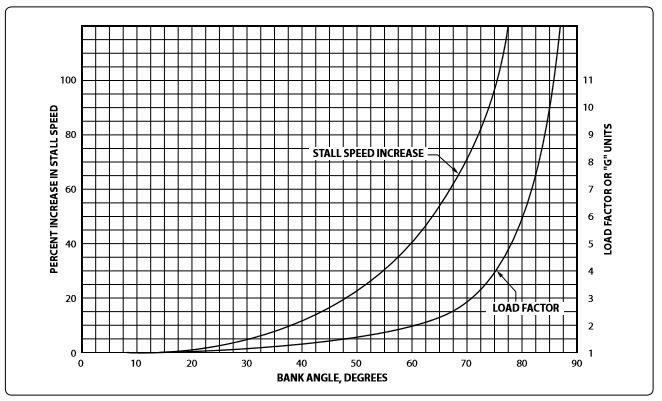 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 78 of 87
78. Question
Refer to figure 4 below. What is the stall speed of an airplane under a load factor of 2.5 Gs if the unaccelerated stall speed is 60 knots?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 79 of 87
79. Question
Refer to figure 4 below. What is the stall speed of an airplane under a load factor of 2 Gs if the unaccelerated stall speed is 60 knots?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 80 of 87
80. Question
Which factor below is the best indication of positive or negative Gs in an aircraft?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 81 of 87
81. Question
Baggage weighing 90 pounds is placed in a no ma! category airplane’s baggage compartment, which 1s placarded at 100 pounds. If this airplane is subjected to a positive load factor of 3.5 Gs, the total load of the baggage would be
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 82 of 87
82. Question
Which of the following would best indicate to the pilot that the load factor placed on the airframe has been increased?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 83 of 87
83. Question
The ratio of an airplane’s true airspeed to the speed of sound in the same atmospheric conditions is
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 84 of 87
84. Question
Transonic airflow typically occurs in airplane speed regimes between Mach
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 85 of 87
85. Question
Acceleration past critical Mach speed may cause compressibility issues such as
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 86 of 87
86. Question
If the airspeed is increased from 89 knots to 98 knots during a coordinated level 45 degree banked turn, the load factor will
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 87 of 87
87. Question
Accelerating past critical Mach may result in the onset of compressibility effects such as
CorrectIncorrect